Perspective
Cloud technologies in TV broadcast

Broadcast television system consists of various processes – first step is acquisition of content, from outside location or in-house creation, post-production activities, packaging, distribution of content, and transmission. Television broacasting technologies are always governed by consumer demand-and-consumption pattern. A long journey of moving from tape-based systems to file-based systems is almost done and giving its positive results. Hardware-based systems have been replaced by software-defined solutions, which are not only cost effective and flexible but also support new formats and functionality, and can be taken up for virtualization effortlessely. SDI transports are replaced with IP stream. IP-based work-flow has become dominant, and it is benefited directly by improvements and innovation in the IT industry.
Proliferation of the smart phone devices, tablets, smart TVs, and connected devices has pushed the requirements of content availability from single place to everywhere, and content distribution in multiple formats at multiple platforms.
All these developments have led to easy adoption of cloud-based technologies by the broadcasters. Cloud-based technology is nothing but delivery of computing power, storage, applications, and other IT resources on demand basis to any business house.
Types of cloud systems
Clouds can be public, private, or both. Deployment of a particular cloud service depends on organizational needs, existing hardware and software systems, current manpower, etc.
Private cloud. The cloud infrastructure is provided exclusively to the organization, which has sole full control on the cloud hardware and software. It can be hosted at organization’s location or at the cloud provider’s data center.
Public cloud. The cloud infrastructure is owned and operated by the cloud provider and is shared by multiple customers.
Hybrid cloud. Hybrid cloud is a mix of both public and private clouds. Secured and critical data is stored in the private cloud for greater security and control. Secondary applications are hosted in the cloud provider’s environment.
Based on the service model, cloud services are classified as SaaS (software-as-a-service), PaaS (platform-as-a-service), and IaaS (infrastructure-as-a service). In IaaS, the responsibility for data stored on the virtual servers belongs to the organization. In case of hacking of data, the organization is responsible for restoring the backups. However, in SaaS, the responsibility of safety of data lies with the cloud provider. For all media organizations, data is very important; therefore, while implementing cloud system, all aspects related to data safety need to be checked thoroughly.
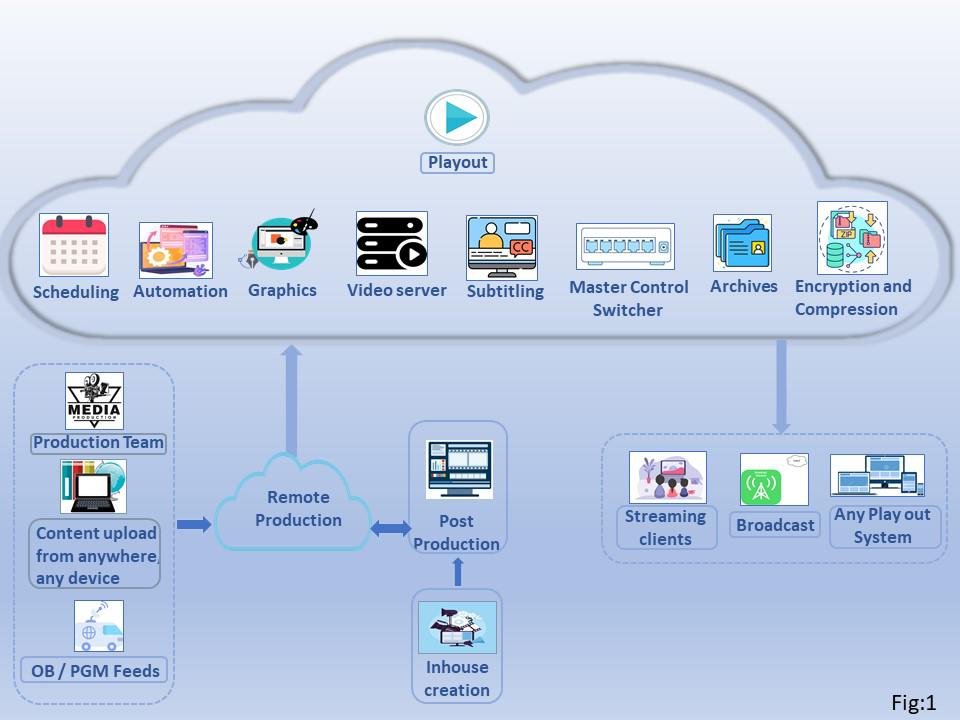
Today’s broadcasters are using clouds for a range of services, which may vary from simple enhanced remote production solutions to complete cloud playout systems. Cloud playout platforms automate many of the processes involved in broadcasting like quality control, creating program schedule, ad insertion, etc.
Advantages of cloud broadcasting
Cost economics. There is no up-front capital cost for broadcasters, and workflow can be easily automated using cloud technology. Cost of maintenance of on-prem servers can also be eliminated. Automating broadcasting processes further reduces cost by cutting manpower requirements. Broadcast companies are shifting their business from CapEx model to OpEx model with cloud technology.
Flexibility and efficiency. In cloud-based systems, video production has become more streamlined. All videos and tools are stored at a single location and can be accessed and shared easily by any authorized user in any part of the world. New footages can be created at any place and can be uploaded quickly in the cloud storage. It gives flexibility of remote operation. In today’s new cycle, these systems give fast access to field officials to upload the content from anywhere in real time, which boosts productivity and efficiency.
Security. Providing security is the most significant responsibility of the cloud managing company. As we all know, content in digital format is more vulnerable to piracy and unauthorized access. But digital technology can make it extremely secure by proper firewall rules, encryption, digital watermarking, geo fencing, etc. Access to cloud servers, services, and storage should be secured with proper access policy and secured protocols.
Scalability. These systems are highly scalable and depending on requirements, resources can be increased or decreased. New pop-up channels or services can be launched quickly and can be decommissioned easily, if not needed.
Outsourcing infrastructure. By deploying cloud solutions in broadcasting systems, hardware can be outsourced and the broadcaster does not need to build and manage their own hardware and need not worry about its day-to-day maintenance. Cloud companies can manage playout systems and storage requirements.
Amazon, Google, Microsoft, IBM, Sony, Oracle, Amagi are some of the big companies leading in this field. Choosing a right cloud provider is critical to any broadcaster. One can look for various factors like cost effectiveness by evaluating the cost of different vendors carefully, reliability which can be checked by track record of uptime, availability, delivery of video without interruptions, and customer support of the company. When working with a cloud service provider, service-level agreements can be reviewed carefully to understand the commitments regarding uptime, support, and security as per broadcasting requirements.
Outlook
Cloud broadcasting provides a flexible, cost-effective alternative to the traditional broadcasting methods and offers seamless viewing experience across various media devices. Commercial model, optimization of existing workflow, data migration, training to staff, latency, redundancy, monitoring and control, etc., are various considerations to be taken care of. The decision to adopt cloud broadcasting depends on a broadcaster’s specific needs, goals, and resources. Conducting a thorough analysis of the potential benefits, costs, and risks associated with cloud broadcasting can help determine if it is the right choice and right time for the broadcaster’s broadcasting strategy.




